Why UK Retirees Shouldn’t Panic Over Trump’s Tariffs and Market Wobbles
If you’ve been watching the news lately, you’ll probably have seen headlines about stock markets taking a tumble thanks to a wave of tariffs announced by Donald Trump. It’s enough to make any retiree feel uneasy – especially if your pension is tied to the markets.
But before you start panicking or making any big changes, take a deep breath. Here’s what you really need to know.
What’s Going On?
President Trump’s tariffs are stoking fears of a global trade war. Investors don’t like uncertainty, and the markets are reacting with volatility. There have been drops not just in the US but across the globe, including here in the UK.
For retirees, that can feel personal. If your pension pot or retirement income is invested in stocks and shares, you might be wondering: Am I going to be okay?
Short answer: Yes, if you stay calm and avoid knee-jerk reactions.
Why This Isn’t the Time to Panic
Markets have always had ups and downs. That’s not new. Whether it was the financial crisis of 2008, the Brexit vote, or the COVID crash (see below), every downturn has sooner or later been followed by recovery.
If you sell investments during a dip, you lock in those losses. But if you ride it out, your portfolio has every chance to bounce back, as has happened before. History is on your side.
Speaking of which…
Consider The Covid Crash
In early 2020 it became clear that COVID was going to be a massive deal, and markets world-wide fell dramatically. And yet by mid-March, as the chart below from Yahoo Finance reveals, they were already recovering.
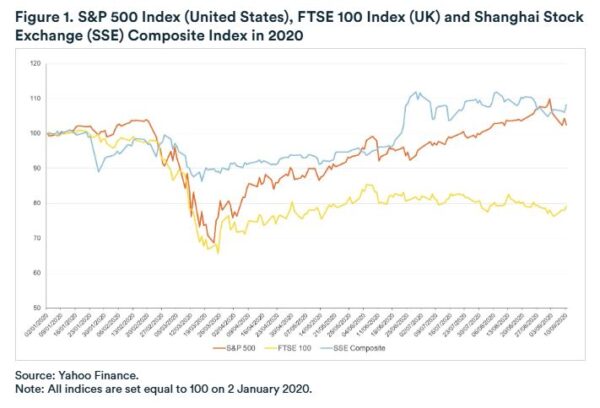 The recovery in stock market values continued through 2021. If you check out my in-depth review of the Nutmeg robo-adviser investment platform, you can see this for yourself. Overall, the period from March 2020 to December 2021 saw a big rise in the value of my Nutmeg investments. If I had panicked in early 2020 and withdrawn all my money then, I would certainly have been thousands of pounds worse off.
The recovery in stock market values continued through 2021. If you check out my in-depth review of the Nutmeg robo-adviser investment platform, you can see this for yourself. Overall, the period from March 2020 to December 2021 saw a big rise in the value of my Nutmeg investments. If I had panicked in early 2020 and withdrawn all my money then, I would certainly have been thousands of pounds worse off.
Your Pension Is Built to Withstand This
Most UK pensions – especially workplace and private pensions – are designed for long-term sustainability. They’re usually diversified across different types of assets like stocks, bonds and property. This helps soften the blow when markets get rocky.
If you have a defined benefit pension, you’re likely shielded from market fluctuations altogether. These pensions pay a fixed income and aren’t directly tied to the stock markets.
For those with defined contribution pensions – the majority of us these days – yes, the value can go up and down. But remember, pensions are managed by professionals who adjust strategies to navigate global changes like the current one.
What You Can Do (Instead of Worrying)
-
Check in with your adviser – They can help you understand how exposed your pension is to current events and whether any changes are needed. See also my article on Why Over-50s May Need an Independent Financial Adviser.
-
Keep a cash buffer – If possible have a few months’ worth of living expenses in cash or savings, so you’re not forced to sell your investments during market lows.
-
Stay diversified – A mixture of investments across regions and sectors helps spread risk.
-
Ignore the noise – Newspaper headlines are designed to grab attention. Focus on your long-term goals instead.
One other point is that, if you’re in the early days of retirement especially, dips can present an opportunity to buy while values are depressed, in the hope of gaining when (hopefully) they recover. This won’t be appropriate for everyone and it’s important to proceed cautiously. Timing the market is notoriously difficult, and if you get this wrong you can lose money rather than making it. But if you are careful (and not overly risk-averse) there are undoubtedly opportunities to be found at these times.
Bottom Line
Trump’s tariffs might be shaking the markets, but your retirement doesn’t have to be shaken with them. Your pension plan is more robust than you might think, and a temporary dip doesn’t mean disaster.
If you’re feeling anxious, that’s normal – but don’t let fear drive your financial decisions. Speak to a financial adviser if you need reassurance (I have one myself), and above all, keep your cool. Retirement is a long game, and a smart strategy will see you through.
As always, if you have any comments or questions about this article, please do leave them below.
DISCLOSURE: I am not a professional financial adviser and nothing in this article should be construed as personal financial advice. If you are uncertain how best to proceed, I strongly recommend speaking to a qualified financial adviser or planner. They will take the time to fully understand your particular circumstances and advise you how best to proceed. All investing carries a risk of loss.












